Rehydrate & Recharge With Our IV Fluids Therapy
IV fluids are solutions injected into veins to treat or prevent dehydration. Intravenous rehydration is a common, safe procedure for people of all ages who are ill, injured, experiencing severe dehydration from heat or exercise, or undergoing surgery. It is also increasingly used in intravenous therapy.
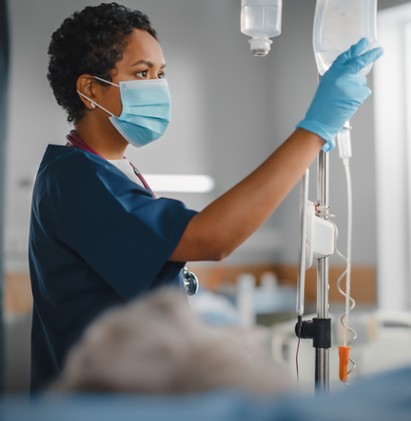

Why are IV fluids (Intravenous Fluids) used?
Water is vital to every cell in our bodies, constituting about 60% of our body composition. Dehydration occurs when the body lacks sufficient water. IV fluids are necessary when someone becomes dangerously dehydrated due to:
- Illness (vomiting and diarrhea)
- Excessive exercise or heat exposure without adequate fluid intake
- Serious injuries or burns
- Surgery, especially when prolonged or accompanied by an inability to consume liquids.
Exploring Different IV Fluids Commonly Used

Water
Water, the universal solvent, is the primary and most abundant fluid in IV bags. Other fluids are typically mixed with water to create the final solution offered to patients. It's important to note that IV bag water is sterilized, eliminating all microorganisms present.

Electrolytes
These, along with water, aid in rehydration. Common electrolytes in IV bags include magnesium, chloride, sodium, and potassium, essential for maintaining normal bodily functions and restoring electrolyte balance in conditions like dehydration.

Minerals
Minerals such as magnesium and zinc support healing processes. They contribute to bone health, immune function, and overall health restoration in patients.
Vitamins
Vitamins like B12, B complex, and C reduce oxidative damage, boost immune function, and enhance brain function. IV administration ensures efficient absorption, especially beneficial for individuals with digestive conditions hindering adequate vitamin absorption.
Glucose
Essential for bodily functions, glucose is administered via IV bags to maintain blood sugar levels, particularly in fasting patients before surgery or those unable to eat due to low blood sugar levels.

Amino Acids
Offering essential nutritional value, amino acids support muscle function and tissue repair. Some, like glutathione and taurine, possess antioxidant properties crucial for cell protection and repair.
Medications
IV therapy administers various medications, including chemotherapy and pain relief for chronic pain or post-surgery recovery.
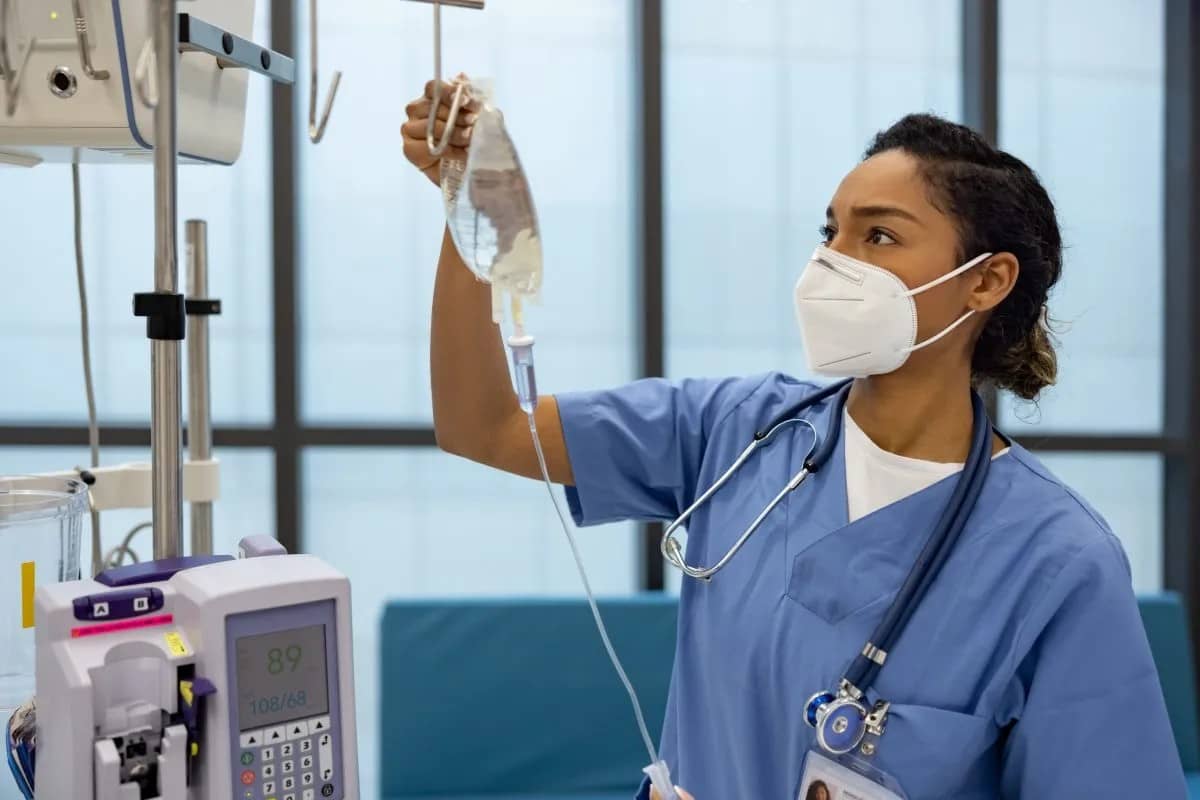

Types of IV Fluids & Their Purposes
- Saline: A common intravenous fluid, saline treats dehydration or electrolyte imbalance, maintaining fluid balance.
- Dextrose Solution: This glucose-water mixture treats low blood sugar levels in patients unable to eat and is used in pre-surgery fasting.
- Lactated Ringer’s Solution: Containing electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and calcium, it treats acidosis, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalance.
- Plasma-Lyte: A balanced electrolyte solution containing calcium, sodium, magnesium, and potassium, it treats severe dehydration, metabolic acidosis, and electrolyte imbalance.
Contact Remedy Pensacola
For further inquiries about IV bag contents and various additives like vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and medications, the experts at Remedy Pensacola are available to assist. Our team comprises highly trained medical professionals, including Registered Nurses and Paramedics, knowledgeable in IV therapy.
IV fluids are necessary when dehydration becomes dangerous, typically resulting from illness, excessive heat or exercise, serious injuries or burns, or surgery hindering oral fluid intake.
Dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution is effective for treating weakness, replenishing extracellular and intracellular fluids and electrolytes.
IV treatment duration varies based on the reason for treatment but typically lasts 45 minutes to an hour. Effects can be immediate or delayed, lasting several days post-treatment.
For moderate to severe dehydration, hospitals or clinics typically administer saline solutions containing glucose, dextrose, and electrolytes.
IV fluids, injected to prevent or treat dehydration, are crucial for intravenous rehydration, aiding individuals who are sick, injured, dehydrated from exercise or heat, or undergoing surgery.
